Note
Click here to download the full example code
Adding a color palette to a figure¶
Plotting a map with a color palette is handled by pygmt.Figure.grdimage. The
pygmt.makecpt method creates a custom color palette that can be used with
the figures and color bars.
import pygmt
# Load sample earth relief data
grid = pygmt.datasets.load_earth_relief(resolution="05m", region=[-86, -64, 17, 24])
Out:
grdblend [NOTICE]: Remote data courtesy of GMT data server OCEANIA [https://oceania.generic-mapping-tools.org]
grdblend [NOTICE]: Earth Relief at 5x5 arc minutes from Gaussian Cartesian filtering (9 km fullwidth) of SRTM15+V2.1 [Tozer et al., 2019].
grdblend [NOTICE]: -> Download 180x180 degree grid tile (earth_relief_05m_p): S90W180
Create a plot with color¶
The pygmt.Figure.grdimage method takes the grid input and optional
region argument to create a figure. It creates and applies a color palette to the
figure based upon the z-values of the data. By default, it plots the map with the
equidistant cylindrical projection and with no frame.
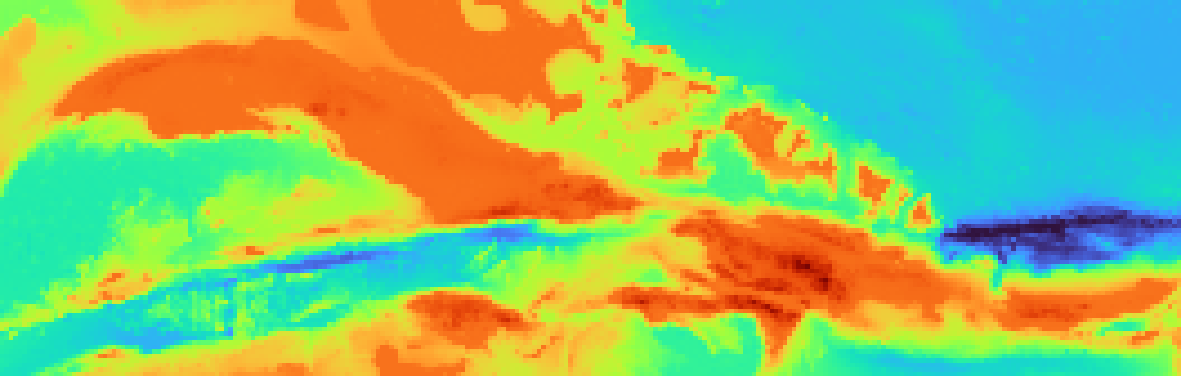
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdimage(grid=grid)
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
A specific color palette can be set using the optional cmap argument for
pygmt.Figure.grdimage. By default, the color palette is set to turbo.
In the example below, the color palette is set to geo.
The full list of color palette tables can be found at https://docs.generic-mapping-tools.org/latest/cookbook/cpts.html.
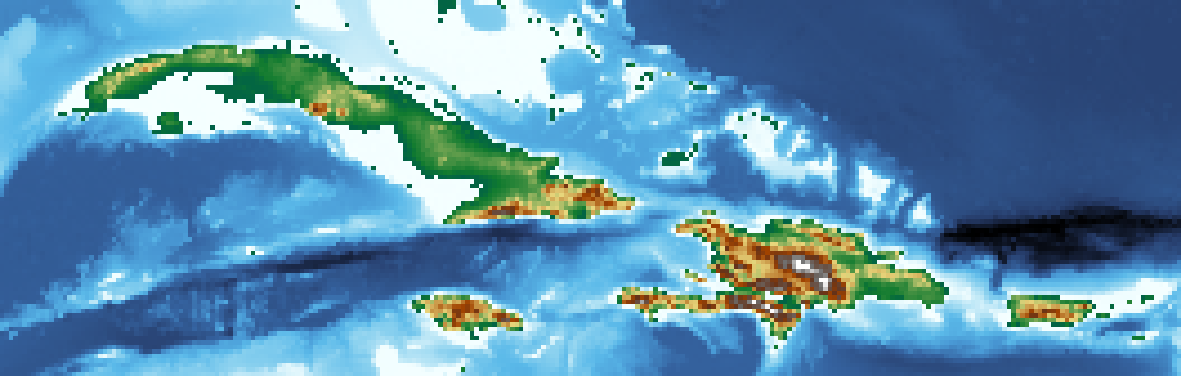
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdimage(grid=grid, cmap="geo")
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
pygmt.Figure.grdimage accepts additional parameters, including frame and
projection.
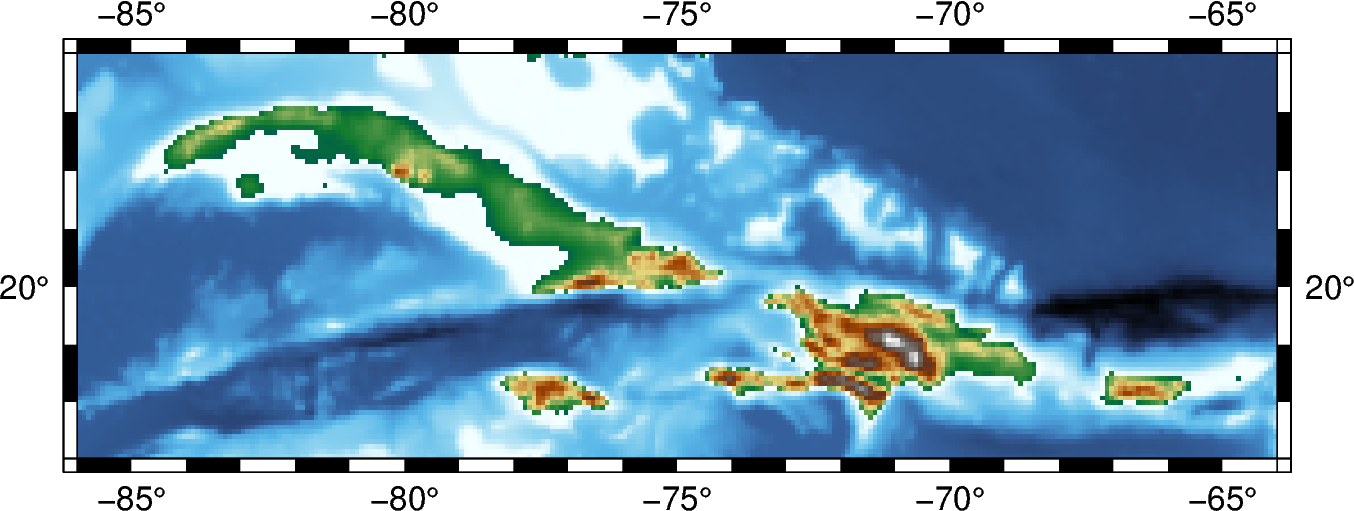
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdimage(grid=grid, frame=True, projection="M6i", cmap="geo")
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
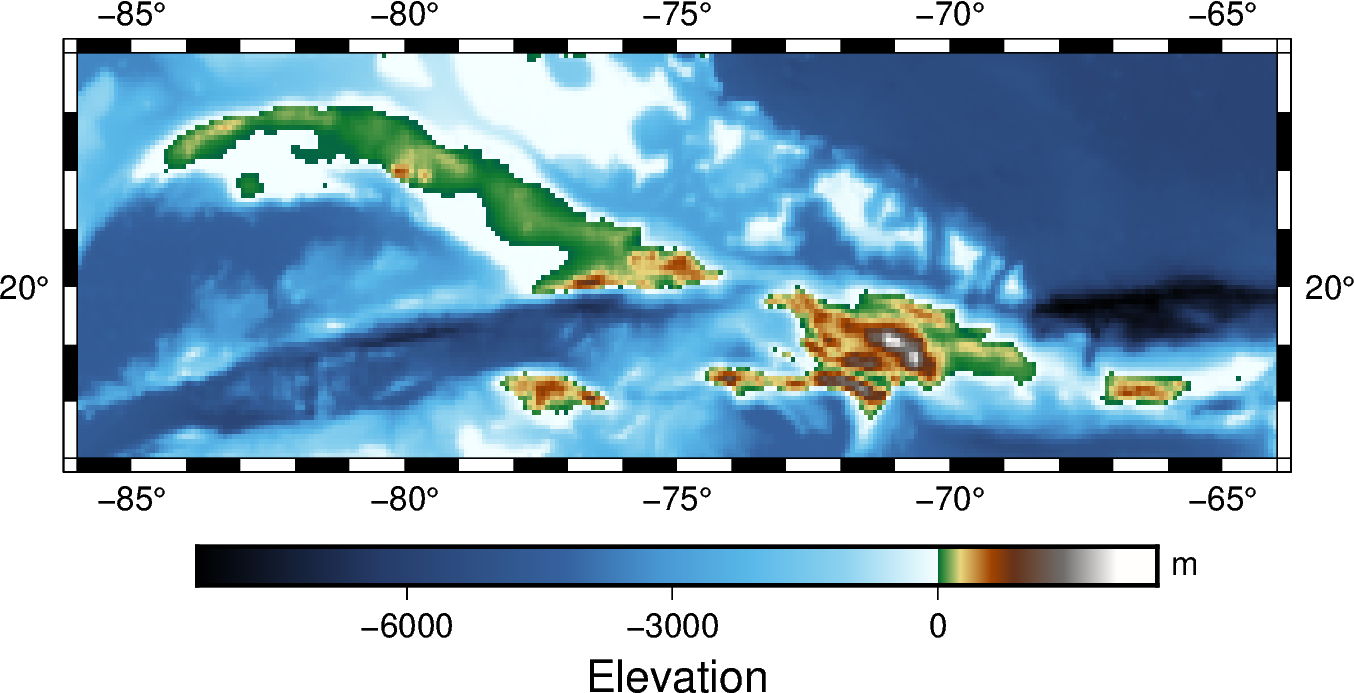
The pygmt.Figure.colorbar method can be used to add a color bar to the figure.
By default, it applies the color palette created by pygmt.Figure.grdimage.
The frame argument can be used to set the color bar labels and intervals.
In the example below, p3000 sets the color bar tick interval to 3,000 meters,
and x+lElevation and y+lm set the x- and y-axis labels for the color bar.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.grdimage(grid=grid, frame=True, projection="M6i", cmap="geo")
fig.colorbar(frame=["p3000", "x+lElevation", "y+lm"])
fig.show()
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Create a custom color palette¶
The pygmt.makecpt method provides the option to create a custom color palette
for a figure. The cmap argument sets the master color palette to base the
new color palette on. The series argument sets the minimum and maximum values, and
optionally the intervals between them; without it, the new color palette defaults to
the min/max values of the master color palette. The series argument can be given
as a string (as below) or as a list series=[-8500, 2500, 1000]. Any values that
fall outside the range of the series will be plotted as black (lower than the minimum)
or white (higher than the maximum).
The pygmt.makecpt method includes an output parameter, which allows the
custom color palette to be saved in a .cpt file. It’s default value is False, which
uses the custom color palette as the default color palette for
the figure and color bar.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="jet", series="-9000/3000", continuous=True)
fig.grdimage(grid=grid, projection="M6i", frame=True)
fig.colorbar(frame=["p3000", "x+lElevation", "y+lm"])
fig.show()
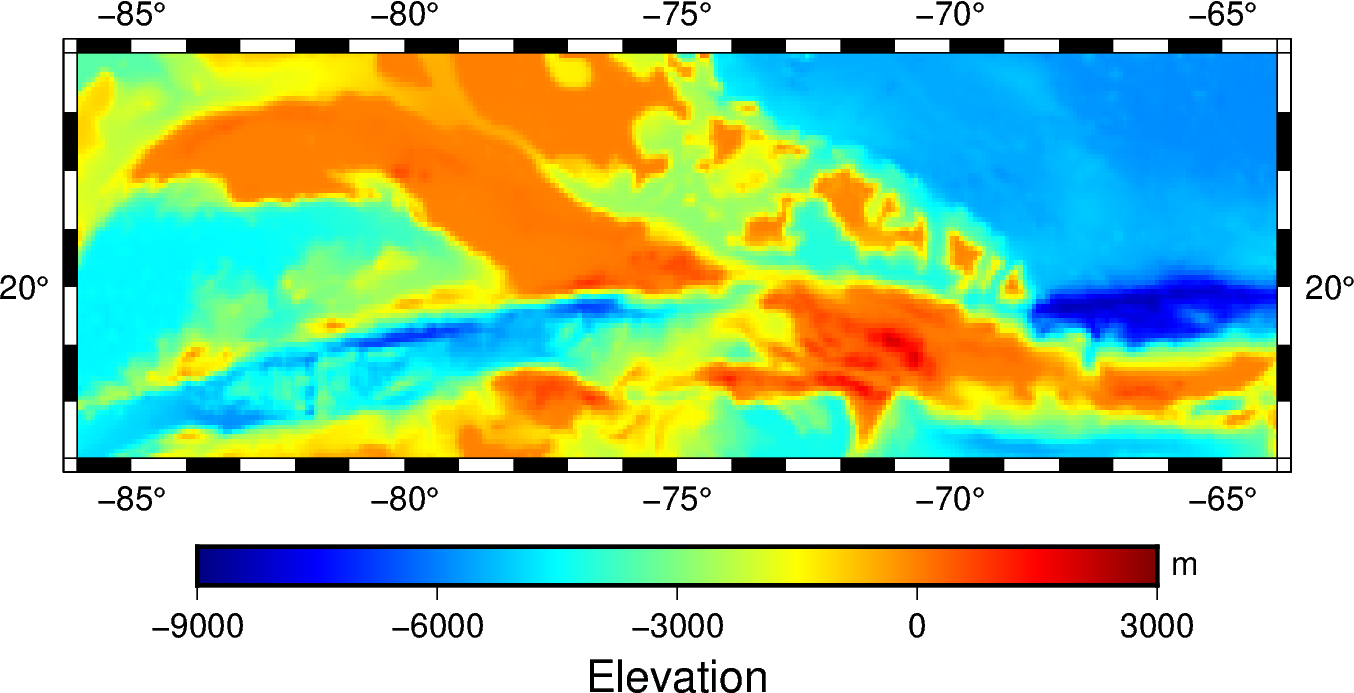
Out:
makecpt [WARNING]: Without inc in -T option, -Z has no effect (ignored)
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
The continuous argument forces the custom color palette to be continuous or
discrete. Discrete color palettes will have a single color for a range of values
within the color palette, while continuous color palettes will assign a different
color for every value in its series. The series argument requires an interval
setting to create a discrete color palette, or it will default to a
continuous color palette.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="jet", series="-9000/3000/1500", continuous=False)
fig.grdimage(grid=grid, projection="M6i", frame=True)
fig.colorbar(frame=["p1500", "x+lElevation", "y+lm"])
fig.show()
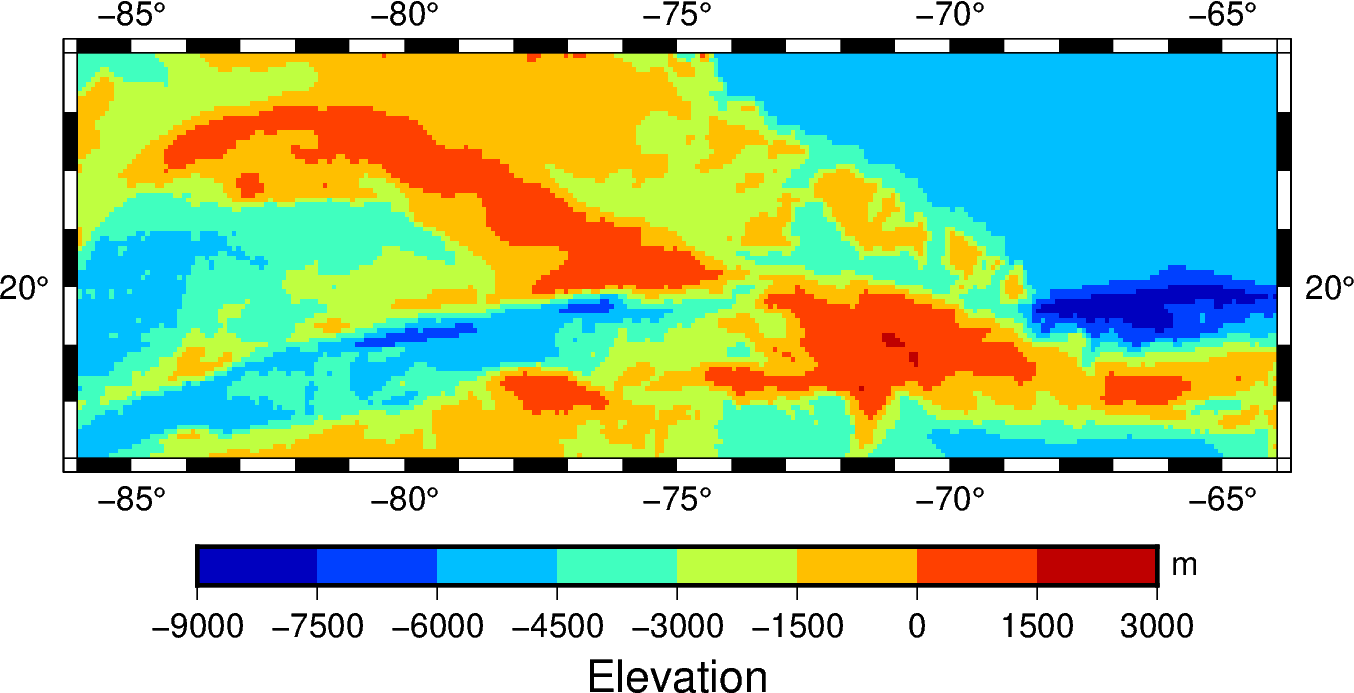
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 6.006 seconds)